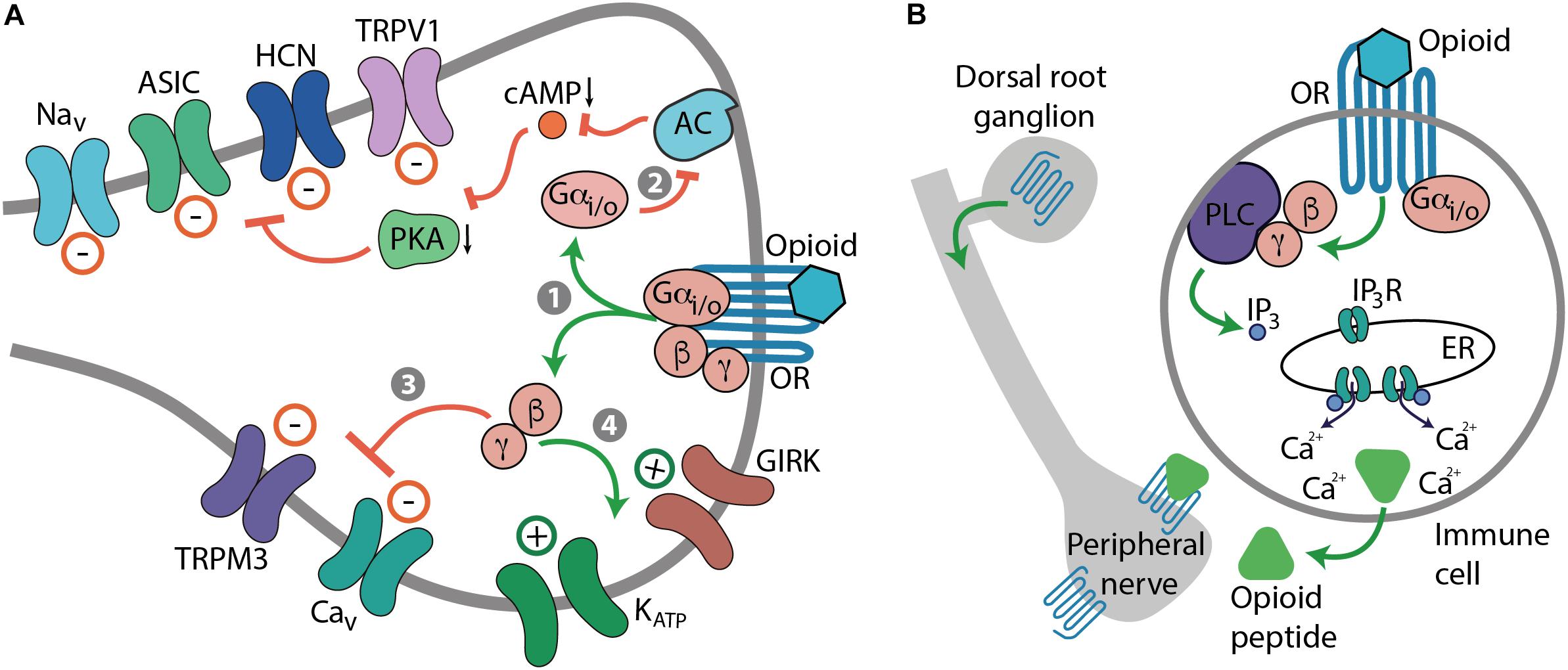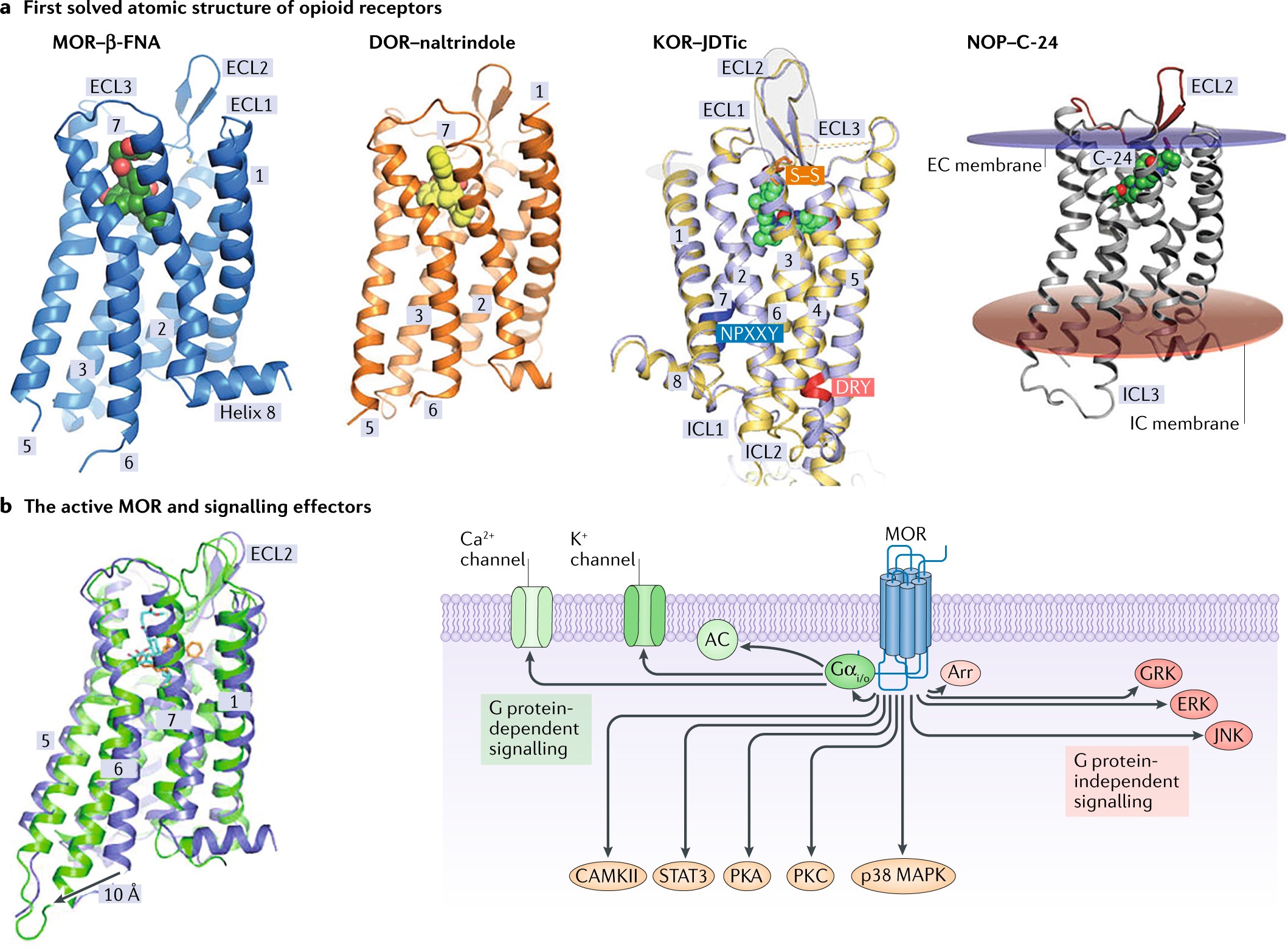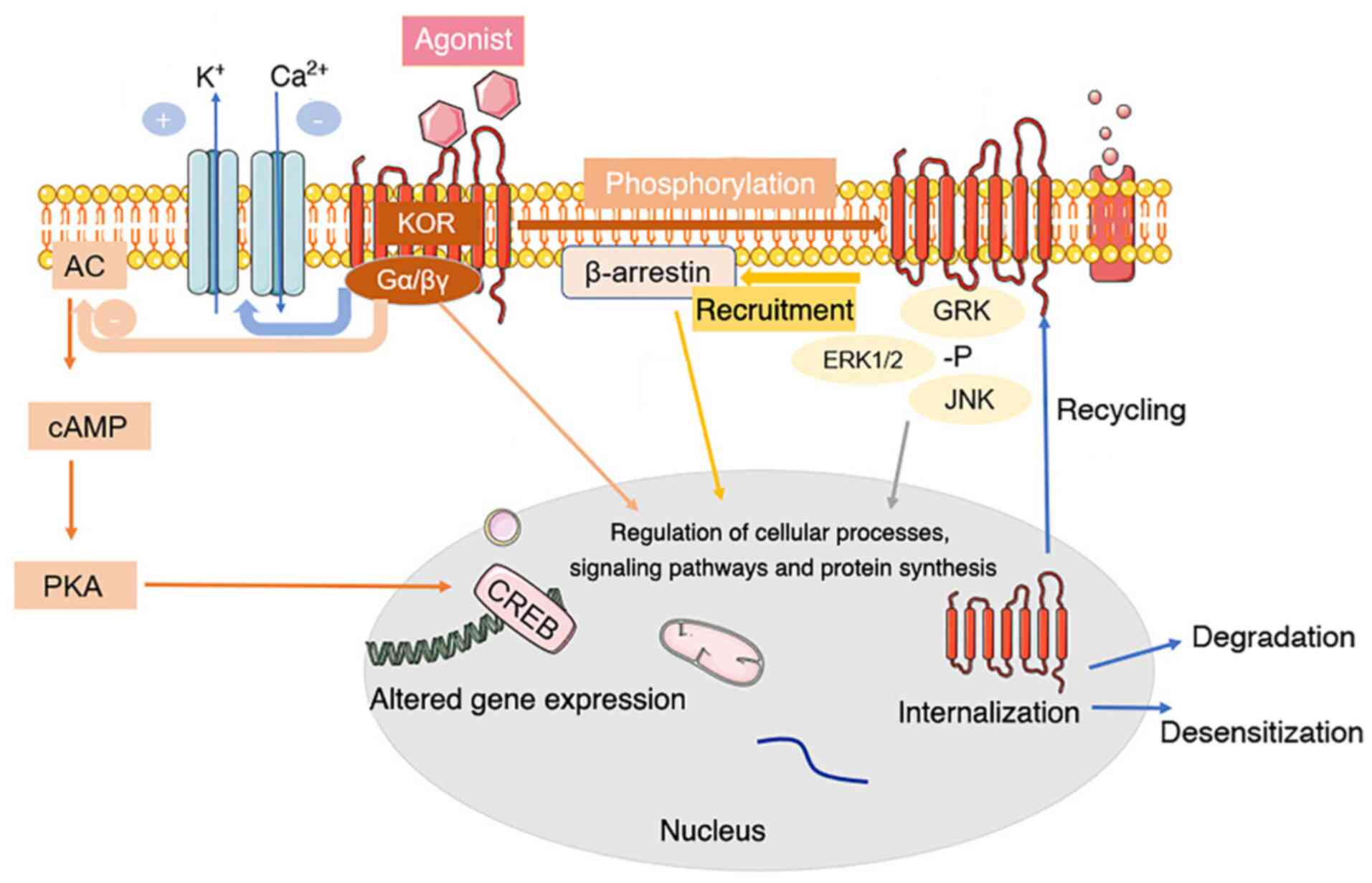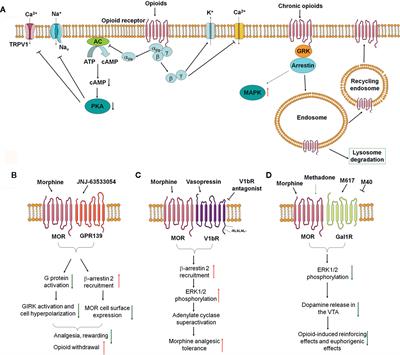
Frontiers | Mu Opioid Receptor Heterodimers Emerge as Novel Therapeutic Targets: Recent Progress and Future Perspective
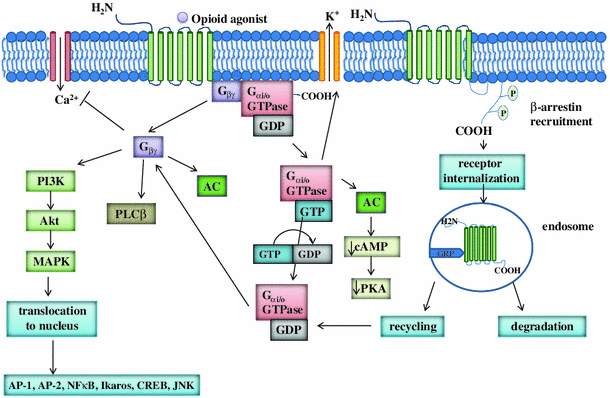
Physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of opioid receptors and their ligands in the gastrointestinal tract: current concepts and future perspectives | SpringerLink

Opioids As Modulators of Cell Death and Survival—Unraveling Mechanisms and Revealing New Indications | Pharmacological Reviews

Discovery of μ,δ-Opioid Receptor Dual-Biased Agonists That Overcome the Limitation of Prior Biased Agonists | ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science

Biased agonists of the kappa opioid receptor suppress pain and itch without causing sedation or dysphoria | Science Signaling

Signaling Properties of Structurally Diverse Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands: Toward in Vitro Models of in Vivo Responses | ACS Chemical Neuroscience

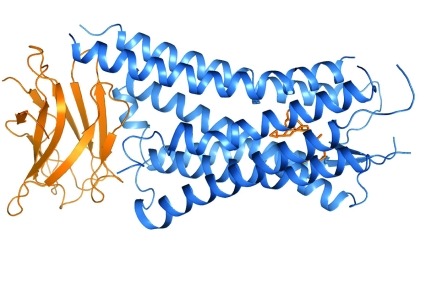
Mu opioid receptor activation enhances regulator of G protein signaling 4 association with the mu opioid receptor/G protein complex in a GTP‐dependent manner - Santhappan - 2015 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
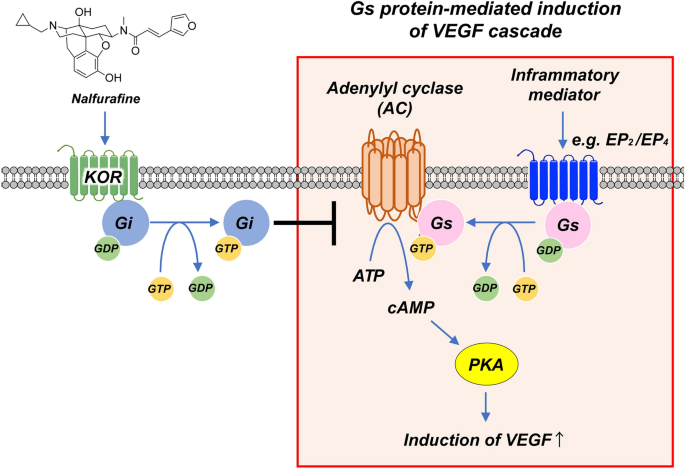
Topical administration of the kappa opioid receptor agonist nalfurafine suppresses corneal neovascularization and inflammation | Scientific Reports
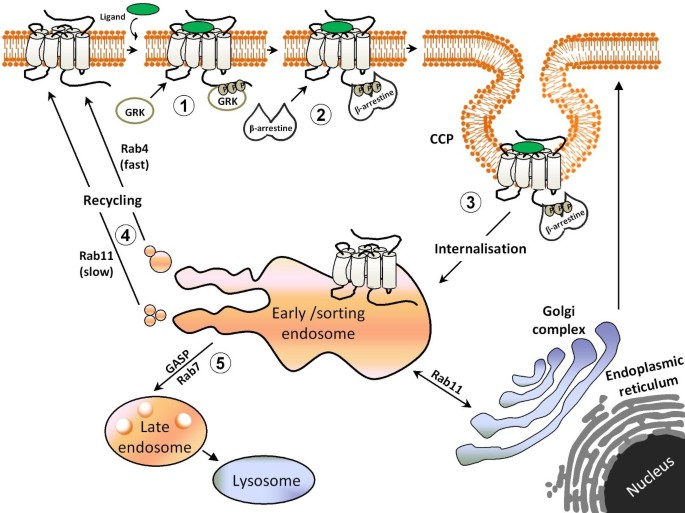
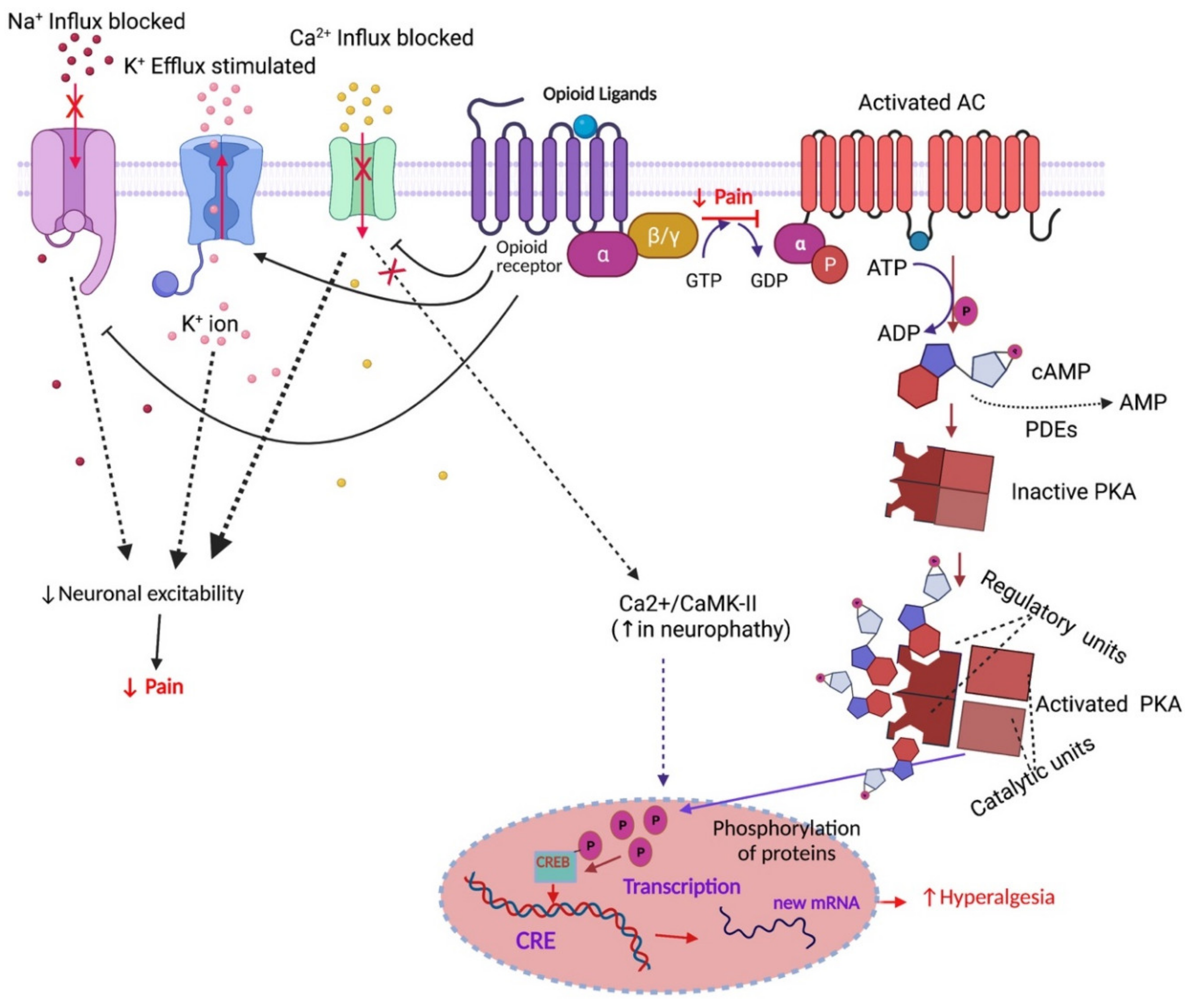
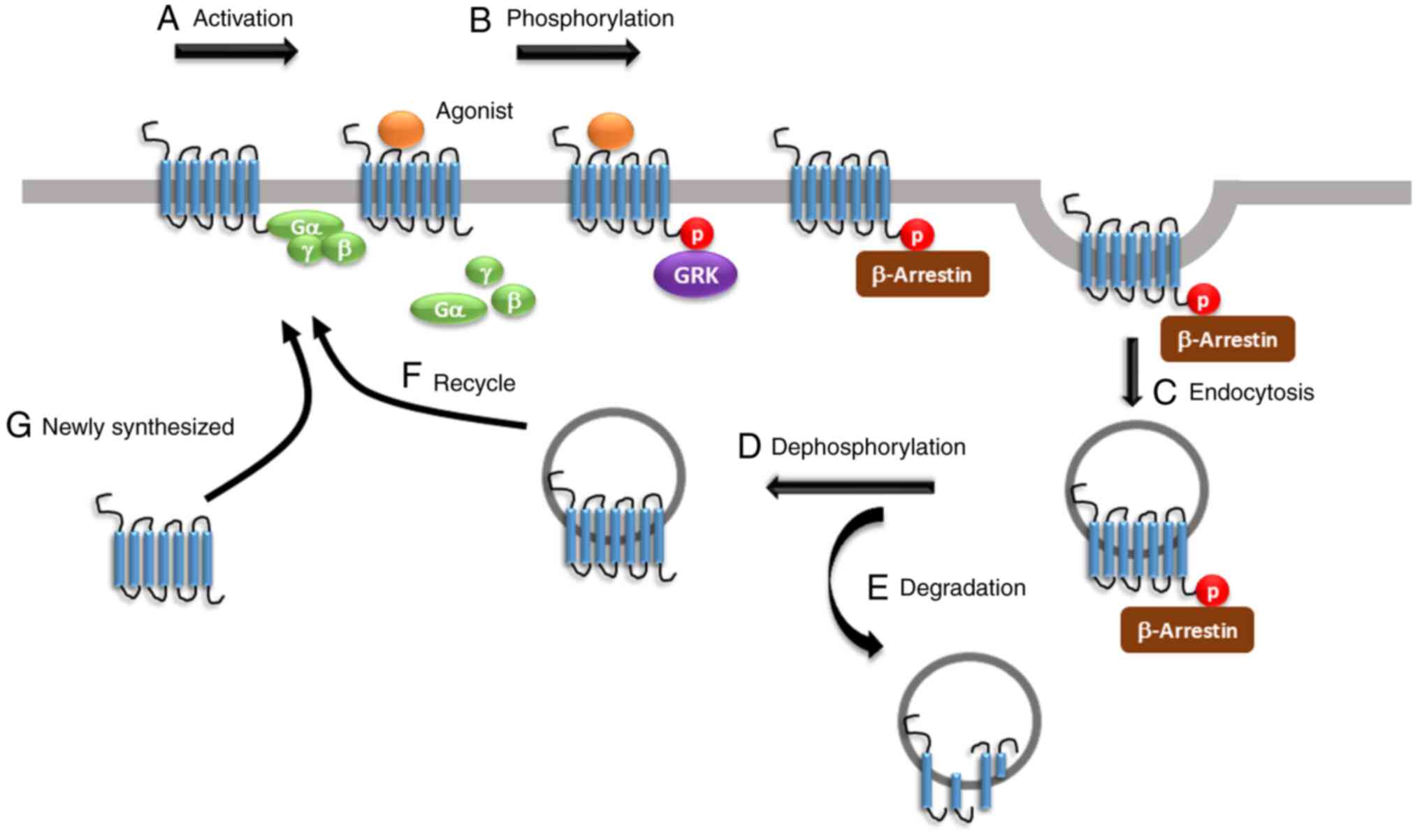
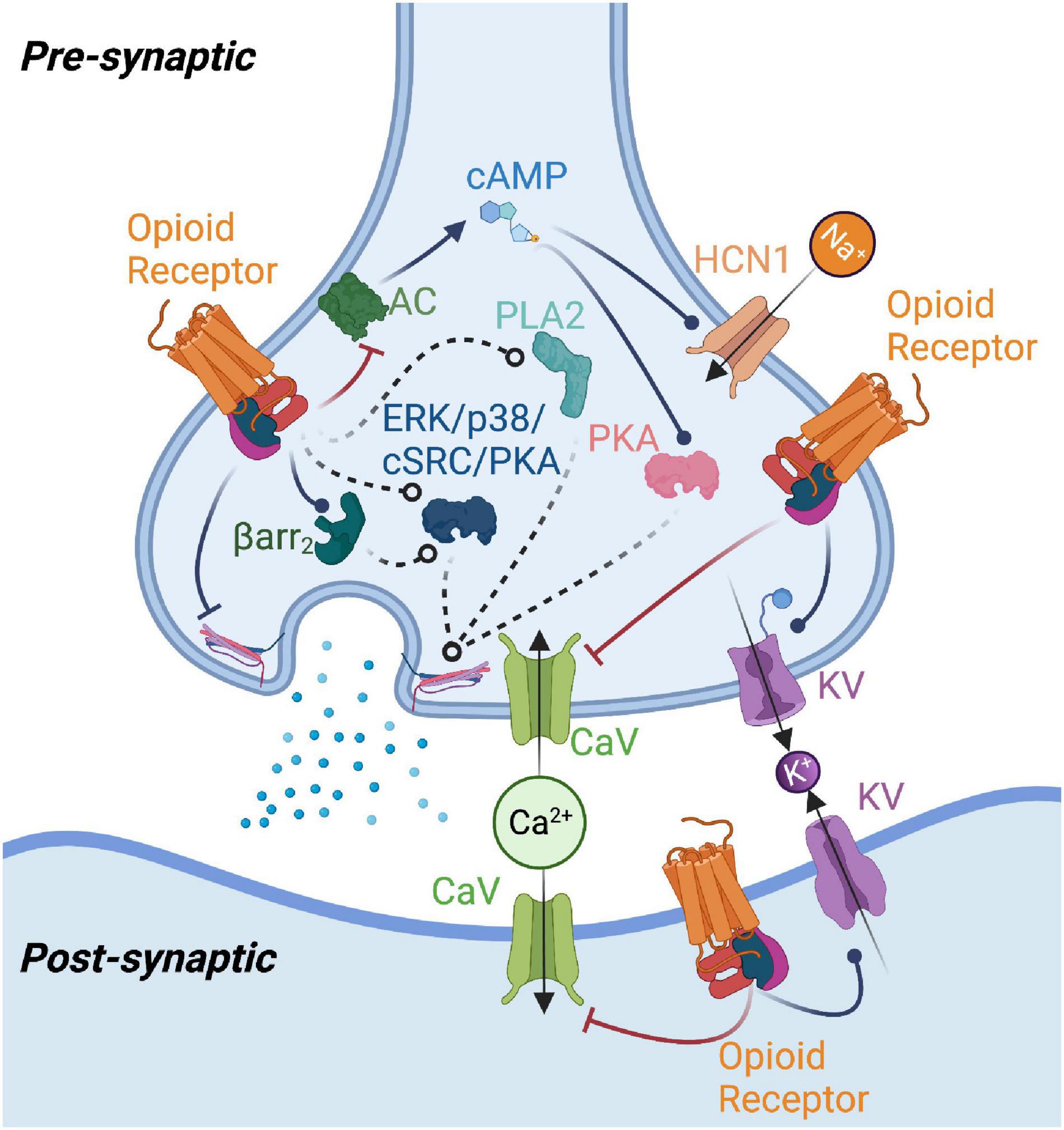
Regulation of opioid receptor signalling: Implications for the development of analgesic tolerance | Molecular Brain | Full Text
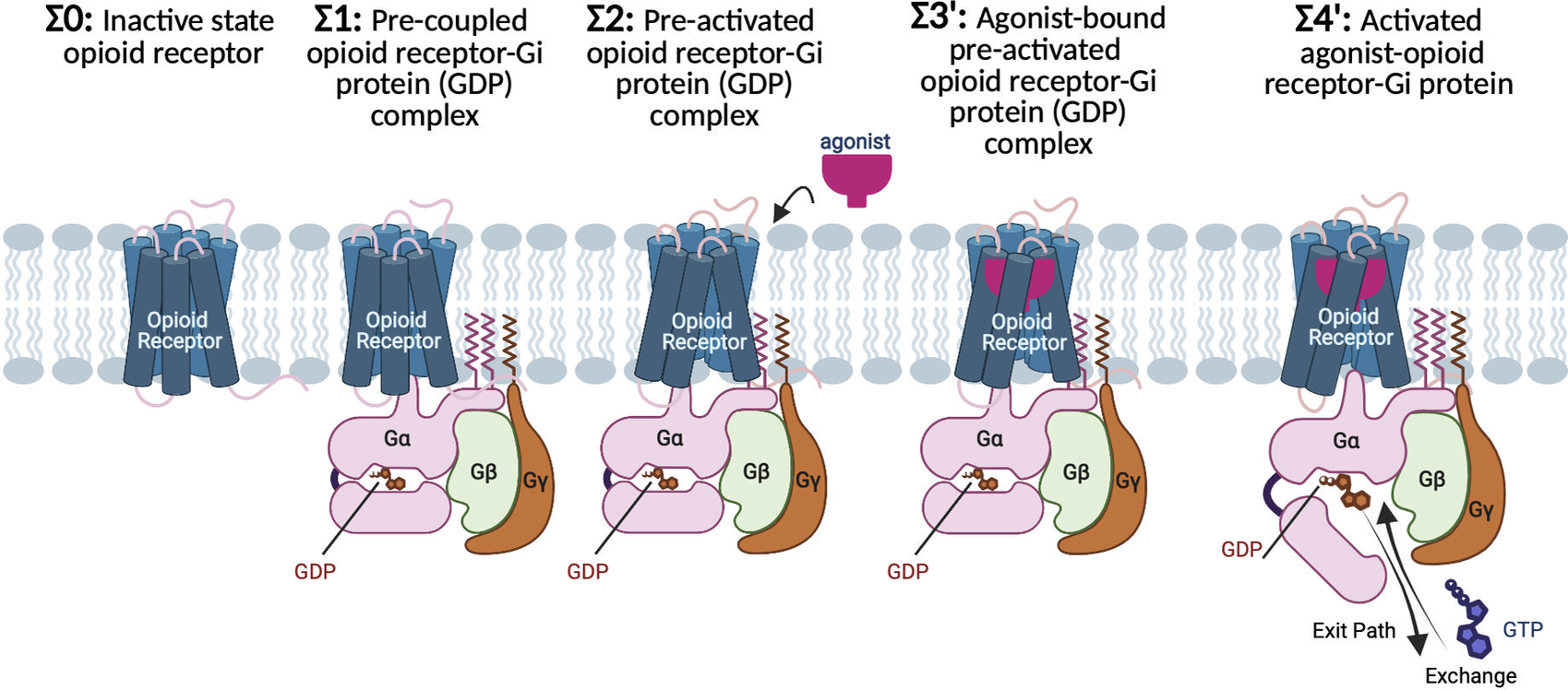
The G protein-first activation mechanism of opioid receptors by Gi protein and agonists | QRB Discovery | Cambridge Core

Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Receptor Signaling in Preclinical Models of Alcohol, Drug, and Food Addiction - ScienceDirect

Elucidating the active δ-opioid receptor crystal structure with peptide and small-molecule agonists | Science Advances
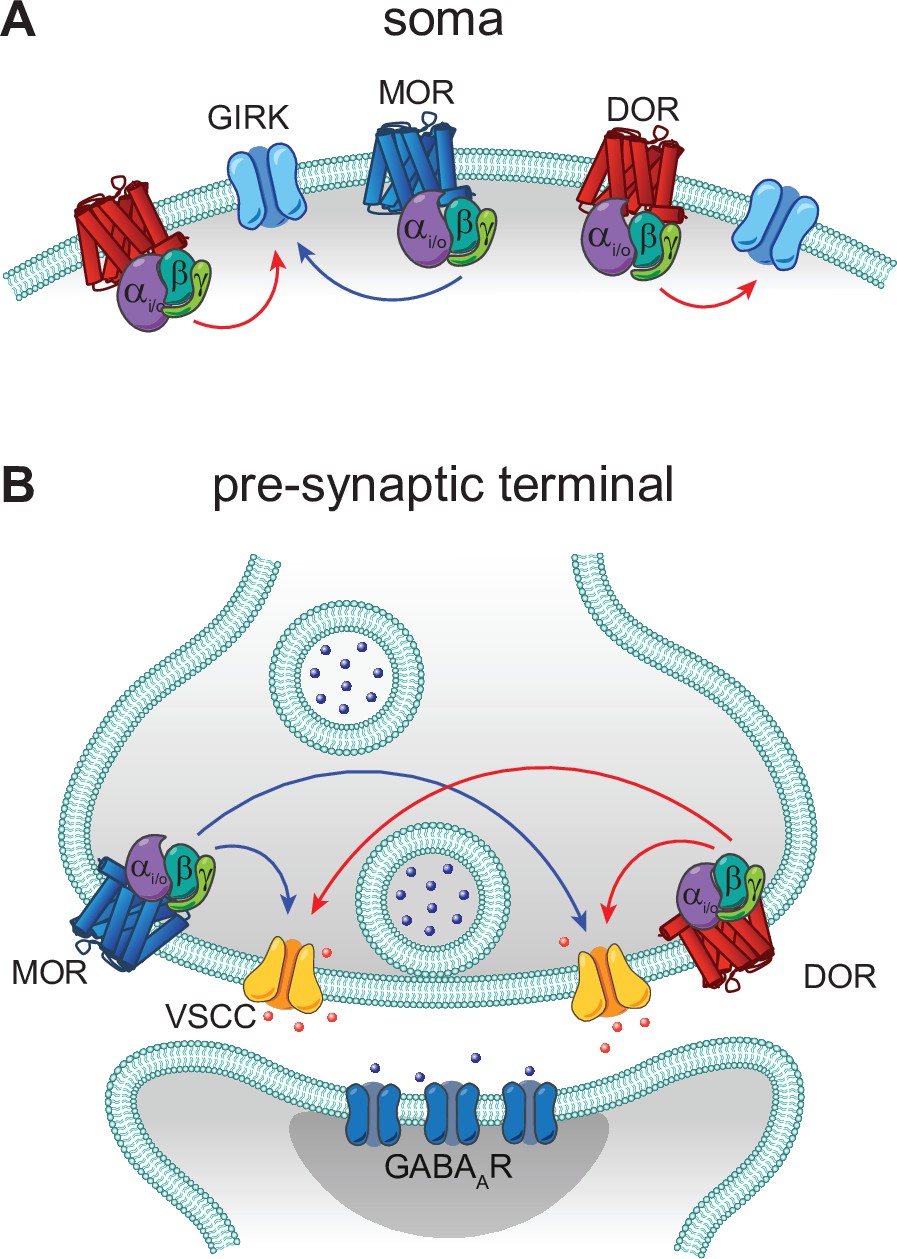
Convergent, functionally independent signaling by mu and delta opioid receptors in hippocampal parvalbumin interneurons | eLife